- Home | Industry Update | Turning Discarded Textiles Into Low-emission Cement: Lithuan...
Turning Discarded Textiles into Low-Emission Cement: Lithuania Unveils a Breakthrough Path for Circular Construction
.webp)
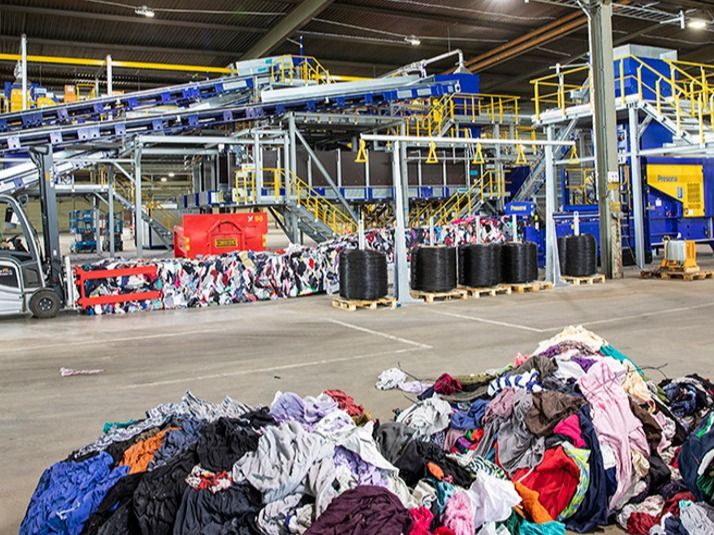
Researchers at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU) in Lithuania have unlocked a remarkable new pathway for circular innovation, turning textile waste into clean fuel and low-emission cement materials. This breakthrough offers a fresh lifeline for Europe push toward greener construction and more responsible textile waste management.
Europe continues to grapple with mountains of discarded garments, much of which ends up in landfills due to mixed fibres, dyes and additives that complicate recycling. Seeking a higher purpose for this waste, KTU scientists discovered that heating textiles at around 300 °C in an oxygen-free environment produces carbon-rich granules. With strong calorific value, these granules can function as alternative fuel, cutting dependence on fossil resources while keeping waste out of disposal sites.
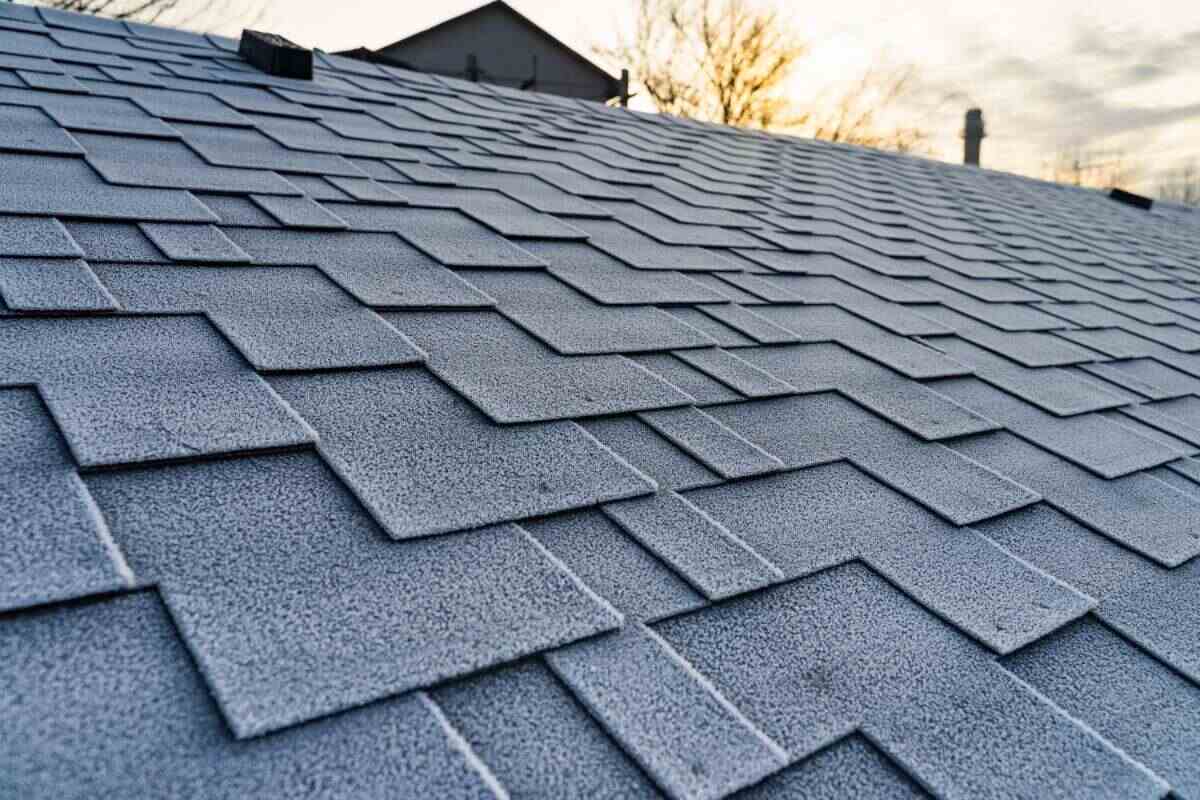
Their research goes a step further by showing how textile waste can actively strengthen cement. Cement production alone contributes up to 8 percent of global CO2 emissions, mainly through energy-intensive clinker. By adding about 1.5 percent polyester fibre from discarded clothing, concrete gains a stunning 15–20 percent rise in compressive strength along with better resistance to freeze–thaw cycles. This makes the improved material ideal for exterior and high-stress infrastructure applications.
A second innovation arises from the ash generated during the combustion of textile-derived fuel. KTU has shown that replacing up to 7.5 percent of cement with this ash can increase compressive strength by as much as 16 percent. This directly lowers clinker usage, bringing down emissions while giving textile waste a meaningful second life.
This work forms part of the Textifuel project by KTU and the Lithuanian Energy Institute, demonstrating how textile and construction industries can unite for circular, low-carbon solutions. As Europe tightens environmental regulations, textile-enhanced cement emerges as a promising pathway for architects, engineers and builders striving to create structures that are both resilient and sustainably designed.
02:49 PM, Dec 04













1.webp)








1.webp)


1.webp)
1.webp)
1.webp)



1.webp)

1.webp)

.webp)





1.webp)




1.webp)











1.webp)











1.webp)


1.webp)

1.webp)



































1.webp)







1.jpg)























































.png)









.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)








1.jpeg)