Smart Monitoring Technology in Warp Knitting Machines: Revolutionizing Textile Production
Share Post
The textile industry has always been a dynamic interplay of tradition, innovation, and adaptability. Among its most sophisticated technological advancements, warp knitting machines have consistently stood out, offering unmatched flexibility, speed, and precision in fabric production. Historically, these machines relied heavily on mechanical precision and human expertise, with operators manually controlling guide bars, yarn feeds, and tension to produce intricate patterns. While effective, this approach had its limitations: inconsistencies in fabric quality, higher wastage, and labor-intensive operations were common challenges. However, the landscape of warp knitting is undergoing a profound transformation through the integration of smart monitoring systems, digital controls and data-driven production management, ushering in a new era of textile manufacturing.
Smart monitoring in warp knitting is more than just automation; it is a convergence of mechanical engineering, digital intelligence and real-time analytics. Modern machines are equipped with sophisticated networks of sensors that monitor every aspect of production, including yarn tension, feed rates, guide bar positions, needle activity, and environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. These sensors communicate continuously with central processing units embedded within the machines, which process the data, detect anomalies, and adjust operational parameters dynamically. For instance, even a minor deviation in yarn tension can trigger immediate corrective actions, preventing defects such as uneven loops, skipped stitches, or fabric distortion. The result is consistent, high-quality fabric output with minimal material waste, a crucial requirement for both fashion and technical textiles.
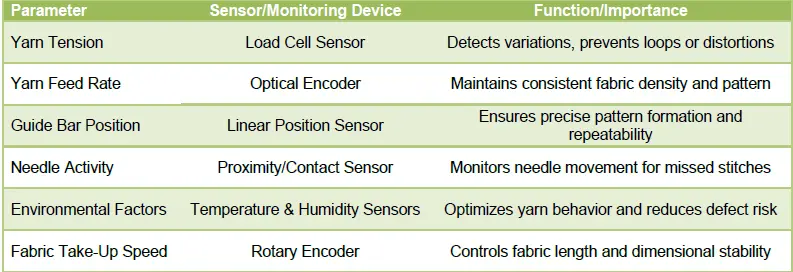
Key Parameters Monitored in Smart Warp Knitting Machines:
At the core of this transformation is digital control technology. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs), microprocessors, and embedded software act as the brain of warp knitting machines, interpreting sensor inputs and executing precise adjustments in real-time. Operators now interact with these systems via intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs), featuring touchscreens, visual dashboards, and real-time performance indicators. This interface not only provides an overview of machine operation but also enables remote supervision, predictive maintenance scheduling, and historical performance analysis. By digitizing control and monitoring, manufacturers gain unparalleled visibility into their production processes, allowing them to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
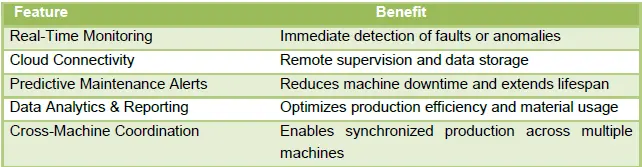
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has taken smart monitoring a step further. Warp knitting machines are now connected to factory-wide networks and cloud platforms, enabling real-time monitoring, data storage, and cross-machine coordination. This connectivity allows production managers to identify inefficiencies, predict maintenance needs, and optimize workflows without being physically present on the factory floor. For instance, if a particular machine exhibits unusual vibration patterns or yarn tension fluctuations, alerts can be sent instantly to supervisors, who can intervene proactively. Such predictive capabilities not only minimize downtime but also enhance the overall productivity of the manufacturing unit.
Benefits of IoT Integration in Warp Knitting Machines:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms have also become integral to smart monitoring. By analyzing vast amounts of operational data, these algorithms identify patterns and correlations that may elude human observation. For example, AI can predict when a machine is likely to produce defects based on historical yarn behavior, temperature fluctuations, or guide bar performance. Over time, the system learns and refines its responses, optimizing machine settings autonomously for maximum efficiency and quality. This not only reduces reliance on human intervention but also ensures that complex fabrics such as spacer fabrics, technical textiles, and multi-layered composites are produced with consistent precision.
Another significant advantage of smart monitoring is its contribution to sustainability. In a textile industry increasingly focused on resource efficiency and environmental responsibility, real-time monitoring reduces waste by identifying and correcting production anomalies immediately. Automated tension control ensures optimal yarn usage, while precise pattern management minimizes discarded fabric. Additionally, energy-efficient operation is facilitated by digital monitoring of machine speed, load, and operational cycles. Manufacturers can track energy consumption, optimize production schedules, and reduce their carbon footprint all while maintaining high standards of fabric quality.
The introduction of smart monitoring has also redefined the role of human operators. Rather than focusing solely on manual adjustments, operators now act as supervisors, analysts, and decision-makers. They monitor dashboards, interpret alerts, and make strategic interventions when necessary, while the machines handle repetitive and precision-driven tasks autonomously. This shift not only increases operational efficiency but also enhances job satisfaction, as workers engage in higher-value tasks that leverage both their technical knowledge and analytical skills.
The evolution of warp knitting machines from purely mechanical systems to intelligent, digitally controlled devices represents a profound technological shift in the textile industry. Central to this transformation is the integration of advanced sensors, which serve as the machine’s senses, providing real-time feedback on every aspect of production. These sensors monitor yarn behavior, guide bar movement, needle positions, environmental conditions, and fabric take-up, creating a continuous stream of data that ensures optimal machine performance. Without such intelligent feedback systems, achieving the precision, consistency, and efficiency demanded by modern warp knitting production would be nearly impossible.
One of the most critical components of smart monitoring is the yarn tension sensor. In conventional warp knitting, variations in yarn tension could lead to defects such as uneven loops, holes, or fabric distortion, which would often go unnoticed until production was complete, resulting in significant waste. Modern load cell sensors measure tension continuously and relay this information to the machine’s central control system. When a deviation is detected, the system instantly adjusts feed rollers or tensioning devices, maintaining uniformity and preventing defects from forming.
The guide bar section of warp knitting machines is another area where smart monitoring is transforming production. Linear position sensors and optical encoders track every movement of the guide bars, which control the looping and interlacing of yarns to form the fabric structure. Misalignment in these bars can disrupt patterns and fabric integrity. Smart monitoring systems detect even microscopic deviations in real time and make immediate corrections, maintaining both pattern accuracy and dimensional stability.
Needle activity is also continuously monitored in modern machines. Proximity and contact sensors detect missed or misfired needles, enabling automatic correction or alerts to operators. This ensures flawless production of even the most intricate fabrics, including tricot, raschel, and spacer textiles. The fabric take-up process, too, is optimized through rotary encoders, which measure fabric speed and length, allowing dynamic adjustments to maintain dimensional stability and fabric density.
Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has further enhanced warp knitting operations. Connected machines communicate with centralized cloud platforms, enabling real-time monitoring, cross-machine coordination, and remote supervision. Production managers can track operational parameters, receive instant alerts, and access historical data for analysis. This connectivity allows for predictive maintenance, enabling operators to anticipate potential failures before they occur and schedule maintenance proactively, significantly reducing downtime and production loss.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are integral to this ecosystem. By analyzing vast datasets, AI detects patterns and correlations that may elude human operators. For instance, subtle deviations in yarn tension or environmental conditions can indicate potential defects. The AI system proactively adjusts machine parameters to prevent errors, continuously learning and refining its responses for improved efficiency and accuracy.
Smart monitoring also facilitates energy optimization. By monitoring motor load, roller friction, and machine speed, the system adjusts operational parameters to reduce energy consumption without compromising production quality. This, combined with optimized yarn usage and reduced defects, enhances both the economic and environmental sustainability of the production process.
Overall, the integration of sensors, digital controls, IoT, and AI has transformed warp knitting machines into intelligent production units capable of self-correction, predictive maintenance, and real-time optimization. These systems ensure superior fabric quality, reduced waste, and greater operational efficiency, embodying the future of warp knitting technology.
The operational success of smart monitoring in warp knitting machines lies in the seamless integration of sensors, digital controls, and AI-driven analytics into the production workflow. Each stage of fabric production, from yarn feeding to fabric take-up, is continuously monitored and dynamically adjusted to maintain high-quality output. This intelligent workflow ensures consistent pattern formation, precise dimensional control, and minimal material waste.
The process begins at the yarn input stage, where advanced sensors measure tension and feed rate before the yarn enters the guide bars. Maintaining consistent tension is crucial because even minor variations can lead to defects such as uneven loops or distorted patterns. Modern monitoring systems instantly detect these variations and adjust feed rollers or tension devices to correct deviations, ensuring uniformity across the fabric.
As the yarn progresses to the guide bar section, linear position sensors and optical encoders track every movement, ensuring that the guide bars follow precise programmed paths. Any deviation, no matter how small, is immediately corrected to maintain pattern accuracy and fabric integrity. This continuous correction is particularly important when producing complex fabrics like spacer or multi-layered textiles, where even a minor misalignment can compromise the entire product.
Needle monitoring is another critical component of the workflow. Sensors detect skipped or misfired needles, triggering immediate correction or alerting operators. This real-time intervention prevents the propagation of defects and ensures continuous, high-quality fabric production. Meanwhile, the fabric take-up process is optimized through continuous monitoring of speed and length. Adjustments are made dynamically to maintain dimensional stability and consistent fabric density.
The integration of IoT allows multiple machines within a facility to communicate with a centralized platform. Real-time data aggregation enables coordinated operation, performance analysis, and remote supervision. If one machine exhibits anomalies in tension or guide bar alignment, nearby machines can adjust accordingly to maintain uniformity across the production line. This level of coordination not only improves efficiency but also minimizes human intervention in repetitive monitoring tasks.
AI plays a crucial role in operational optimization. Machine learning algorithms analyze real-time and historical production data, identifying patterns that may indicate potential defects or inefficiencies. The system proactively adjusts machine parameters to prevent errors, continually learning from production cycles to optimize performance. This intelligent adjustment allows manufacturers to produce highly specialized fabrics with consistent quality while reducing waste and downtime.
Smart monitoring also enhances predictive maintenance. Sensors continuously track motor vibration, needle bar alignment, roller wear, and electrical load. Deviations from normal operating patterns trigger alerts, enabling maintenance teams to intervene before failures occur. This proactive approach extends machine lifespan, reduces downtime, and minimizes production losses.
Energy efficiency is another important aspect of workflow integration. By continuously analyzing load, friction, and machine speed, the monitoring system adjusts operational parameters to minimize energy consumption without compromising output quality. The combination of energy optimization, precise tension control, and AI-driven pattern correction ensures not only economic efficiency but also environmental sustainability.Workflow Enhancements via Smart Monitoring: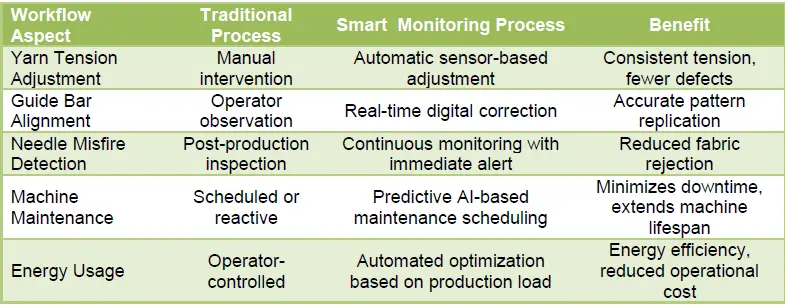
Sangiacomo, a global leader in circular warp knitting, has focused on AI-based process optimization and defect detection. Their machines analyze sensor data to identify subtle patterns indicating potential faults before they affect fabric quality. The integration of AI allows machines to adjust guide bar movements, yarn feed rates, and needle timing autonomously, particularly in complex fabrics like jacquard or spacer structures. This capability is crucial in industries requiring precision fabrics, where even minor errors can result in substantial economic loss.
Another notable trend in real-world implementation is the integration of smart monitoring with production management software. Advanced ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems now communicate directly with machine sensors and digital control units, providing end-to-end visibility of the production process. Factory managers can analyze production efficiency, material utilization, and machine health across multiple units simultaneously. This level of integration ensures that manufacturing decisions are data-driven, optimizing both operational efficiency and product quality. Integration of Smart Monitoring with Production Management:
The adoption of smart monitoring systems also enables customized fabric production. In contemporary textile markets, manufacturers are required to produce highly specialized fabrics with unique specifications. Smart warp knitting machines, with their integrated monitoring systems, allow for rapid pattern changeovers, precise tension adjustments, and automatic defect correction, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands without compromising quality.
In industrial applications, these systems have demonstrated substantial economic benefits. Manufacturers report reduced wastage by up to 30%, energy savings of 15–20%, and improved machine uptime exceeding 95%. Beyond efficiency, these systems enable compliance with stringent quality standards required for technical textiles in automotive, medical, and aerospace sectors.
The integration of smart monitoring systems in warp knitting machines is not merely a technological upgrade; it represents a fundamental shift in how the textile industry approaches production, quality control, and operational efficiency. As the global textile sector moves toward Industry 4.0, smart monitoring plays a pivotal role in connecting machines, processes, and operators in a seamless, data-driven ecosystem. The future of warp knitting lies in the convergence of automation, artificial intelligence, real-time data analytics, and sustainability, reshaping the industry for both industrial and apparel applications.
A primary trend in the future of smart monitoring is the expansion of predictive and prescriptive analytics. Current AI systems already analyze real-time and historical data to predict potential defects and maintenance needs. In the coming years, these systems are expected to evolve further, offering prescriptive solutions that not only anticipate issues but also recommend or autonomously implement optimal corrective actions. For example, if environmental fluctuations are likely to affect yarn behavior, the system could automatically adjust guide bar positions, tension levels, and machine speed to prevent any defect, ensuring consistent fabric quality without human intervention.
Another future direction is enhanced machine connectivity and integration with factory-wide digital ecosystems. Warp knitting machines will increasingly be connected through IoT-enabled networks that facilitate real-time communication between multiple production units. This connectivity allows for coordinated operations across entire production lines, enabling synchronized fabric output, optimized resource allocation, and predictive load balancing. Factory managers will have the ability to monitor, control, and analyze production from a centralized platform, even remotely, making operational decisions faster and more precise.
Sustainability is emerging as a critical driver of smart monitoring adoption. Textile production has historically been resource-intensive, consuming large amounts of energy, water, and raw materials. Smart warp knitting machines reduce waste by automatically correcting defects, optimizing yarn usage, and minimizing energy consumption through precise machine control. Predictive maintenance further contributes to sustainability by extending the life of machine components and preventing unnecessary replacements. As environmental standards and consumer expectations evolve, the ability of smart monitoring systems to deliver eco-efficient textile production will become a decisive competitive advantage.
The strategic impact of smart monitoring also extends to customization and market responsiveness. In an era where consumers demand highly specialized fabrics with unique patterns, textures, or functional properties, the agility provided by smart monitoring is invaluable. Manufacturers can adjust production parameters quickly, switch patterns seamlessly, and maintain consistent quality for bespoke fabrics. This capability enables rapid response to market trends, faster product launches, and reduced lead times, aligning warp knitting operations with modern supply chain demands.
Artificial intelligence will play an increasingly central role in process optimization and autonomous decision-making. Beyond defect detection, AI systems will optimize production sequences, energy consumption, and yarn utilization. Continuous learning algorithms will allow machines to refine operational parameters based on past performance and evolving material characteristics. This will enable warp knitting machines to handle diverse fabric types, including high-performance technical textiles, medical textiles, and advanced composites, with unparalleled precision.
Workforce roles will also evolve alongside technology. Operators will transition from manual controllers to strategic supervisors and data analysts, responsible for interpreting machine insights, overseeing AI-driven decisions, and managing production workflows. This shift not only increases efficiency but also elevates human skill sets, aligning workforce capabilities with advanced digital manufacturing requirements.
The future of smart monitoring in warp knitting also includes integration with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) tools for training, maintenance, and process visualization. Operators could use AR interfaces to monitor machine performance, receive guided maintenance instructions, or visualize fabric formation in real time. Such technologies will further reduce human error, improve training efficiency, and enhance the overall production environment.
05:04 PM, Jan 02
Source : Smart Monitoring Technology in Warp Knitting Machines: Revolutionizing Textile Production


.webp)


.webp)




